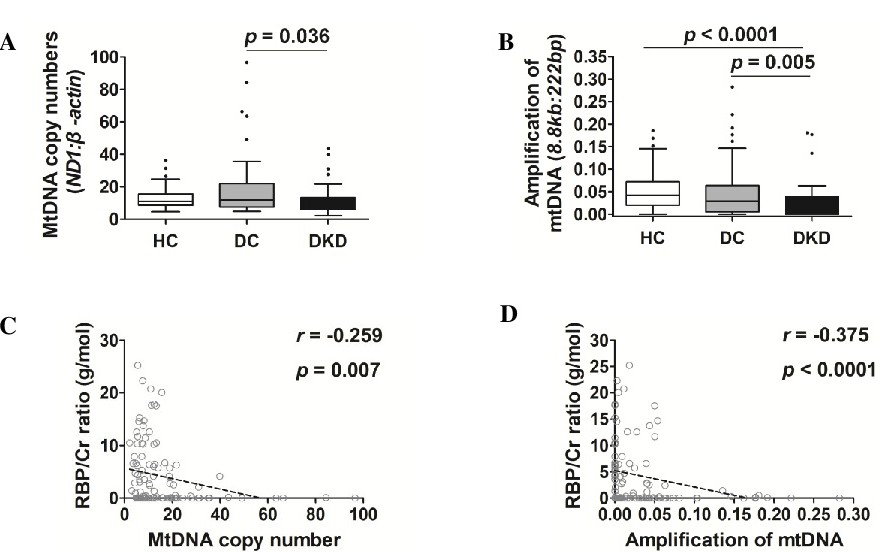
Fig. 1. MtDNA damage was increased in serum of DKDs. DNA were isolated from serum of HCs (n=65), DCs (n=48) and DKDs (n=60). (A) MtDNA copy numbers in DKD patients were significantly decreased compared to DC patients. A real time qPCR was carried out to determine mtDNA copy numbers as mitochondrial (ND1) to nuclear (β-actin) ratio. (B) Damaged mtDNA was significantly increased in DKD patients. DNA damage was quantified using the elongase method. The relative amplification was quantified by normalizing the fluorescence values of the long PCR product (8.843 kb) to the short PCR product (222 bp). (C and D) Correlation analysis revealed mtDNA copy number and amplification of mtDNA was negatively correlated with RBP /Cr ratio, respectively. r, correlation coefficient. RBP, retinol-binding protein; Cr, creatinine; HC, healthy control; DC, diabetic control; DKD, diabetic kidney disease.